Planting and Growing
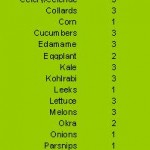
How long do seeds last?
Seed Viability Keep your seeds stored properly and they will last more than just one season. Rodale’s Garden Encyclopedia says this about seed storage: “Storage in the dark is preferable to storage in the light.” and “For most seeds, a relative humidity of 50-60 percent and a temperature between 32 and 50 degrees Fahrenheit …
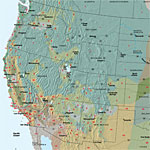
Hardiness Zones
How much cold a plant can tolerate is conveyed by using plant hardiness zones. Each zone has a 10 degree Fahrenheit difference in the average annual minimum temperature. For example, the lowest average temperature in Zone 3 is -40 to -30 degrees Fahrenheit, while the lowest temperature in zone 10 is +30 to +40 degrees …
Seed Germination
Getting seeds to germinate isn’t an exact science, but some general knowledge of the science helps to get seeds off to a great start. Water, air, light Seeds need to be moist to germinate. At planting time, water the seedbed, plant the seeds to the depth that is stated on the seed packet, and then …
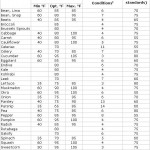
To know when to plant, take your soil’s temperature.
Soil – not air – temperature is the trigger for seed germination. Soil temperature changes gradually. Factors that affect the process include the soil’s exposure to sunlight, its texture, moisture content and surface level (low-lying, flat or mounded). Gardeners can expect particular soil temperatures to bring particular results. Most cool-loving garden vegetables germinate only when …
Hardening Off Plants
What is cutin and why is it important when hardening off plants and preventing sunscald? The outside layer of plant leaves is protected by a layer of epidermis, which functions similarly to human skin. In this epidermis, there is a layer of cutin, which is a waxy substance that protects the leaf from dehydration. The …
The Importance of Plant Spacing
An adequate space between your plants will reduce competition for light, will conserve water, and will provide more soil nutrition to each plant. There is a limit to the amount of nutrients in your soil. By leaving plenty of room between plants, they can have a wide area from which to draw their sustenance. Keeping …
Crop Rotation – My Easy Method
The goal with crop rotation is to fool the pests and diseases that may have learned where their favorite food (your crops) is. My method of crop rotation also takes into account the fertility needs of the soil. The method is to rotate between three areas. Legumes, heavy feeders, and light feeders. Legumes (peas and …
Pollination
Vegetables that are eaten past the flowering stage rely on proper pollination. If there’s a problem with this vital process, vegetable production will suffer. Below are descriptions of vegetables that rely on pollination, the pollination method they use, and possible problems and solutions. Squash – Squash plants have male and female blossoms on each plant. …
Brix and Growing for Flavor
Gardeners can measure the brix in their vegetables for an indication of the success of their crop. Brix is a measurement of flavor and sweetness. Brix is not new. It was Professor A.F.W. Brix, a German chemist who discovered in 1870 that the sweetness of grape juice could be measured before the juice was made …
Watering the Garden
Plants rely on water as an essential element for successful growth. Here are some watering tips: The best time to water is in the early morning. Watering during the middle of the day can result in wasted water due to evaporation from wind and/or heat. Avoid watering in the evening and letting the plants remain …